Use cases
Spinal Cord Toolbox
Spinal cord toolbox (SCT) is an open-source analysis software package for processing MRI data of the spinal cord [De Leener et al. 2017]. ivadomed is SCT’s backbone for the automated segmentation of the spinal cord, gray matter, tumors, and multiple sclerosis lesions, as well as for the labeling of intervertebral discs.
Creation of anatomical template
ivadomed was used in the generation of several high-resolution anatomical MRI templates [Calabrese et al. 2018, Gros et al. 2020]. To make anatomical templates, it is sometimes necessary to segment anatomical regions, such as the spinal cord white matter. When dealing with high resolution data, there may be several thousand 2D slices to segment, stressing the need for a fully-automated and robust solution. In these studies, only a handful of slices were manually-segmented and used to train a specific model. The model then predicted reliably and with high accuracy (Dice score > 90%) the delineation of anatomical structures for the thousands of remaining unlabeled slices.
Tumor segmentation
ivadomed also proves to be useful in the context of clinical radiology routine REF, where clinicians need to segment tumors, edema, and cavity to establish prognosis and monitor the outcome. The framework is composed of a cascaded architecture that detects the spinal cord, crops the image around the region of interest, and segments the tumor (Figure herebelow). The resulting model can be applied to new data using only CPUs, which is more convenient in the clinical setting. The advanced features and architectures available in ivadomed, such as FiLM, were pivotal in obtaining encouraging results despite the difficulty of the task and the relatively low number of images.
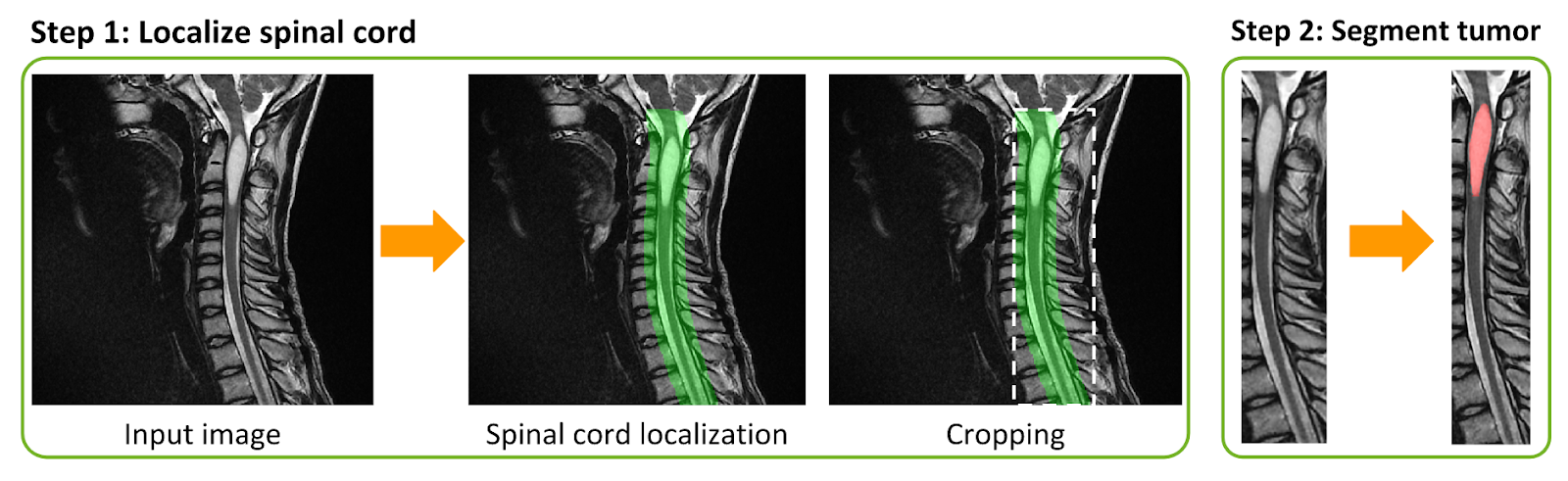
Fully automatic spinal cord tumor segmentation framework. Step 1: The spinal cord is localized using a 3D U-Net and the image is cropped around the generated mask. Step 2: The spinal cord tumors are segmented.
AxonDeepSeg
AxonDeepSeg (ADS) is an open-source analysis software package for segmentating and computing morphometry on microscopy data of nerve fibers [Zaimi et al. 2018]. ivadomed is ADS’s backbone for the automated segmentation of axons and myelin on scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM; Figure herebelow) and bright-field optical microscopy (BF) images.

Automatic axons and myelin segmentation on TEM input image.